What are the NFPA Standards for Commercial Fire Protection?
Fire protection is highly regulated and technically complex. Commercial fires cause billions in property damage each year and pose serious risks to life, property, and legal liability. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) establishes standards to ensure businesses implement proper systems to prevent these outcomes.
As fire protection technology evolves, so do the NFPA’s requirements. Business owners and facility managers must stay informed and compliant as these changes occur. Read on to learn about the most important NFPA codes for commercial buildings, how each one makes facilities safer, and what can happen if you fall out of compliance.
What is the NFPA?
The NFPA is an international nonprofit founded in 1896. Its goal is to reduce fire and life safety risks through research, education, and code development. The NFPA publishes and regularly updates more than 300 codes and standards. These guide everything from fire alarms and suppression systems to emergency planning and building egress. Authorities having jurisdiction (AHJs) use these codes to design and enforce safer buildings.
Which NFPA codes apply to commercial fire protection?
NFPA commercial fire protection codes are crucial for commercial facilities. Not every code applies to every building, but most fall under several core standards that govern fire alarms, sprinklers, extinguishers, and system maintenance. Compliance depends on factors like building size, occupancy, hazard level, and the systems installed. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most important standards relevant to commercial fire safety and building compliance.
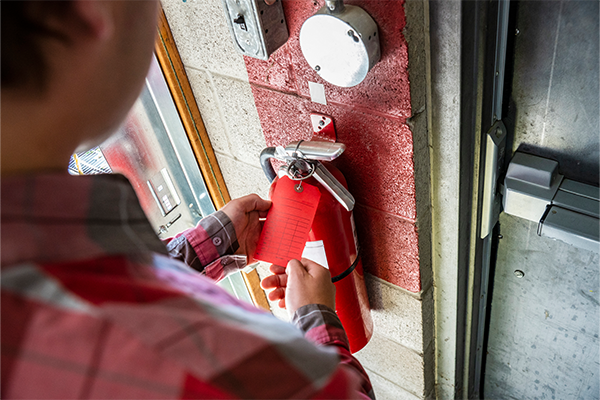
NFPA 10—Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers
Portable fire extinguishers are a frontline defense against small fires. NFPA 10 requires that they be properly selected, installed, inspected, and maintained. The standard also requires employee training and documentation. Improper placement or outdated equipment often leads to compliance violations. This also means missed chances to put out small fires before they grow.
NFPA 10 outlines requirements for:
- Fire extinguisher categorization for fire classes
- Installation height, placement, and accessibility
- Inspection, testing, and annual maintenance
- Recordkeeping and tagging procedures
- Employee fire extinguisher training
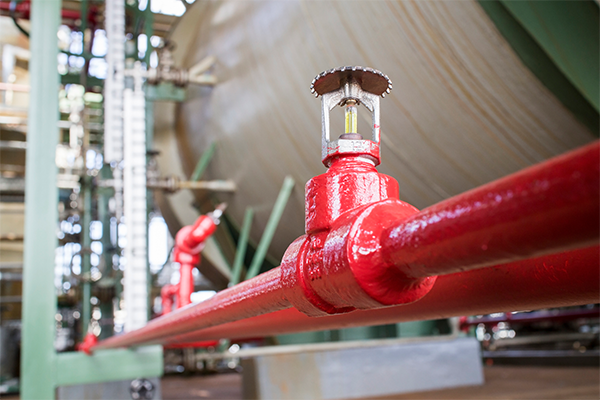
NFPA 13—Standard for the Installation of Sprinkler Systems
NFPA 13 is the industry standard for commercial fire sprinkler system design. It ensures sprinkler systems work by specifying layout, spacing, water supply, and hydraulics. Sprinklers control fires and often suppress flames before firefighters arrive. NFPA 13 minimizes property loss and protects lives.
NFPA 13 governs requirements such as:
- Types of sprinkler systems (wet, dry, pre-action, deluge)
- System layout, spacing, and obstruction rules
- Hydraulic calculations and water supply requirements
- Sprinkler system components and installation methods
- Standards for special hazard and high-pile storage configurations
NFPA 25—Standard for the Inspection, Testing & Maintenance of Water-Based Fire Protection Systems
NFPA 25 defines the requirements for inspecting, testing, and maintaining fire sprinklers, fire pumps, standpipes, and water tanks. Even a well-designed system can fail if it’s neglected or not tested properly. NFPA 25 helps prevent these failures by setting maintenance intervals and testing methods. AHJs often audit NFPA 25 records as proof that a building’s fire protection systems were maintained correctly.
NFPA 25 sets inspection and maintenance requirements for:
- Sprinklers and sprinkler piping
- Fire pumps and controllers
- Standpipe systems
- Water storage tanks
- Backflow prevention devices
- Valves, flow switches, and tamper switches
NFPA 72—National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
NFPA 72 is a foundational code for commercial fire protection. It governs the design, installation, monitoring, testing, and maintenance of fire alarm systems. As fire alarm technologies evolve, NFPA 72 is updated regularly to reflect new safety practices and inspection standards. Facilities using fire alarms or emergency communication equipment must follow this code to stay compliant and keep occupants safe.
NFPA 72 covers the following areas:
- System design and equipment requirements
- Fire alarm installation and performance
- Emergency communication and mass notification
- Testing, inspection, and maintenance schedules
- Monitoring and reporting requirements
- Integration with elevators, HVAC, and life safety systems
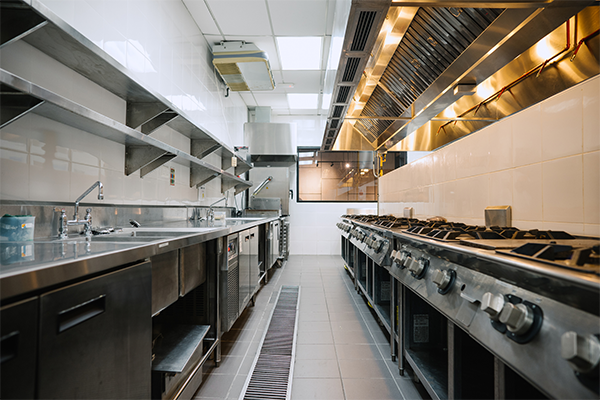
NFPA 96—Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations
The restaurant industry and other commercial-grade kitchens represent the highest cause of commercial fires due to grease accumulation, high heat, and continuous cooking. NFPA 96 establishes standards for kitchen hood systems, grease exhaust ducts, and cooking-related fire suppression systems. Consistent cleaning and documented maintenance are essential because grease fires can spread rapidly through ductwork, causing catastrophic damage.
NFPA 96 requirements include:
- Hood and duct design and installation
- Grease exhaust ventilation standards
- Cleaning frequency and documentation
- Automatic fire suppression system performance
- Interconnection with gas and electrical shutoff controls
NFPA 101—Life Safety Code
NFPA 101 focuses on protecting building occupants. It establishes rules for safe egress, fire-rated barriers, occupancy classifications, and emergency lighting. Unlike many other NFPA standards, NFPA 101 applies to both new and existing structures. It is widely adopted and often forms the basis for building codes. NFPA 101 is especially important for large facilities with vulnerable populations or tall buildings with high occupancy.
NFPA 101 covers life safety requirements related to:
- Egress routes and exit signage
- Fire-rated walls, doors, and barriers
- Occupancy classifications and load limits
- Emergency lighting and illumination standards
- Protection for high-risk or vulnerable populations
NFPA 2001—Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems
While NFPA 2001 isn’t required for every commercial building, it’s essential for structures with water-sensitive equipment. This code sets design, installation, safety, and maintenance rules, including concentration limits, response times, and safety standards for occupied spaces. These systems are found in data centers, museums, healthcare facilities, and other commercial sites that prioritize fire protection without potential water damage.
NFPA 2001 regulates:
- Approved clean agent types and applications
- System design parameters and discharge calculations
- Safety limits and human exposure guidelines
- Inspection and maintenance requirements
- Enclosure integrity testing (door fan testing)
What are the common NFPA commercial compliance gaps?
Even well-managed facilities can miss key NFPA requirements. These omissions leave them vulnerable to AHJ citations, equipment failure, or liability issues. Many compliance gaps occur because systems weren’t installed to code, weren’t maintained, or aren’t up-to-date with current standards.
Common NFPA compliance gaps include:
- Missed or overdue inspection, testing, and maintenance
- Blocked, painted, or damaged fire sprinkler heads
- Lack of documentation or incomplete service records
- Improper fire extinguisher placement or expired tags
- Disabled fire alarm notification appliances
- Changes in building layout or occupancy, but not system designs
- Inadequate emergency lighting or obstructed egress paths
Are there penalties for failing to comply?
Non-compliance with NFPA standards carries significant consequences for building owners and operators. AHJs, insurance carriers, and fire marshals may impose corrective actions, financial penalties, or even temporary shutdowns. Beyond regulatory consequences, non-compliance increases risks to life, property, and business operations.
Potential penalties for NFPA non-compliance include:
- Fines issued by fire marshals or local authorities
- Required immediate corrections at the building owner’s expense
- Business interruption orders or occupancy restrictions
- Increased insurance premiums or loss of coverage
- Denied insurance claims following a fire event
- Legal liability for injuries or property loss
- Civil lawsuits in cases of negligence
Protect your facility with NFPA-compliant solutions from FSS Technologies
Staying compliant with NFPA standards is an ongoing responsibility, not a one-time project. Building conditions change, equipment ages, and codes evolve, and documentation must be maintained consistently. Partnering with certified fire protection experts ensures every system in your facility meets current NFPA requirements and performs when it matters most.
FSS Technologies delivers fire and life safety services that meet the latest NFPA standards. Our NICET-certified technicians design, install, inspect, test, and maintain systems for all industries. We keep your business protected and compliant year-round. Contact us to schedule a system evaluation or ask about NFPA standards for your building.