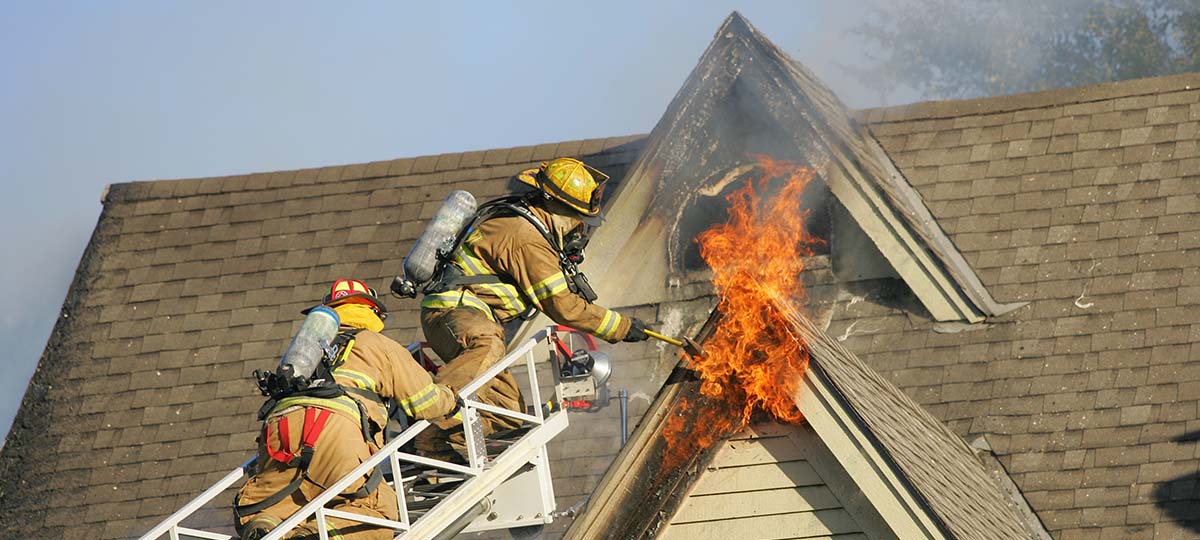
Fire Systems for the Manufacturing Industry
Few industries face as many fire safety concerns as manufacturing does, and the consequences of poor fire safety can be catastrophic. From 2017 to 2021, roughly 36,784 fires occurred yearly at industrial or manufacturing properties, causing $1.5 billion in direct property damage. With materials prone to combust or explode, industrial businesses must take extra care to protect their employees. Learn about manufacturing fire safety standards from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and how they influence the components of a fire system for an industrial environment.
What NFPA codes apply to the manufacturing industry?
Manufacturing facilities handle various materials, from food products to vehicles and anything in between. The NFPA has published over 80 codes addressing fire hazards and safety techniques for industrial settings.
Manufacturers must also follow universally applicable codes like:
- NFPA 1 – Fire Code
- NFPA 10 – Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers
- NFPA 13 – Standard for the Installation of Sprinkler Systems
- NFPA 70 – National Electric Code
- NFPA 72 – National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
- NFPA 101 – Life Safety Code
Depending on the types of substances your business handles, different NFPA codes may determine the configuration of your commercial fire safety system. Here are several examples of codes that cover industrial settings that handle various materials.
Manufacturers dealing with liquids that are more prone to catching or starting fires should familiarize themselves with NFPA 30. The code outlines the different classes of liquids based on their boiling point or flash point. Consultations from authorities or engineering evaluations help identify and mitigate a specific facility’s fire and explosion hazards.
Any industrial facility that creates organic, chemical-based paints and inks must adhere to the requirements outlined in NFPA 35. This code specifies guidelines for a building’s construction, equipment, maintenance, and fire safety measures. Fire prevention and protection methods vary based on the type of materials being created and the presence of ignition sources.
NFPA 51B applies to manufacturing environments that depend on processes that generate sparks, flames, or heat. The code mainly emphasizes the required responsibility and awareness of those directly participating in or supervising hot work. Additional sections cover the necessary precautions for protective clothing, fire extinguishers, and factors that determine whether hot work is permissible for specific areas.

Operations that store, manage, or process agricultural and animal products, by-products, and other similar materials must abide by NFPA 61. In addition to covering assessments and tests that identify potential material and equipment hazards, this code discusses how personnel and authorities can prepare to prevent or suppress fires. One of the unique tests outlined in this code is a dust hazard analysis (DHA), which evaluates fire and explosion risks in conveyors, bucket elevators, and other similar machinery. This code will eventually be consolidated as part of NFPA 660, Standard for Combustible Dusts.
Any business that uses industrial-grade equipment should follow the requirements listed in NFPA 79. This code addresses potential fire and electrical hazards from using high-powered machinery. Guidelines for wiring, power sources, user controls, and more are clearly outlined to protect those who use and work around these devices.
NFPA 654 covers safety measures for industrial facilities that handle combustible materials in small pieces. The code covers requirements and processes that help reduce the risk of injuries or loss of life due to flash fires or explosions. Buildings and equipment must be in specific configurations to ensure inhabitants can escape. Like NFPA 61, this code will be consolidated with others in NFPA 660.
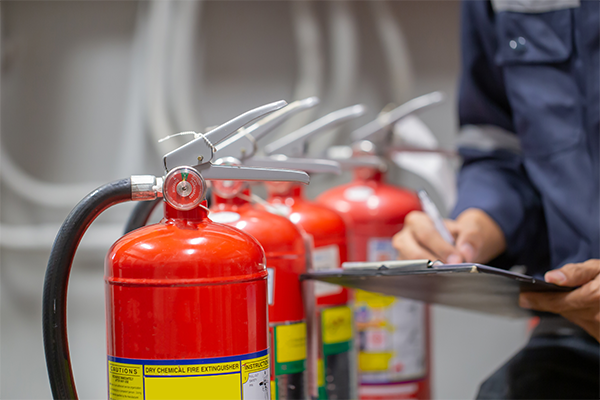

What should an industrial fire system include?
With many unique hazards to consider in a manufacturing environment, having a fire system that protects your employees and operations is essential. Depending on the materials your facility handles, you may need a more customized system that ensures every risk is mitigated or prepared for. Here are some components that every industrial fire system should leverage.
Passive fire protection is vital in industrial settings, where heavy machinery and hazardous materials can make firefighting more complex. Walls, barriers, and doors with sufficient fire ratings are critical for preventing flames from spreading to other areas of the plant. These elements provide valuable time for personnel to evacuate and for firefighters to control the situation. By isolating fires, these structures also prevent rapid escalation and limit the damage to other parts of the plant.
Fire alarm systems are the heart of an effective fire protection strategy in manufacturing facilities. These systems detect hazards early and notify workers, allowing for swift evacuation or suppression efforts. A well-designed alarm system should incorporate a combination of manual and automatic alarms and strategically placed smoke detectors and pull stations throughout the plant. Systems should also include emergency lighting and signage to ensure anyone inside knows their evacuation options.
Fire extinguishers allow workers to tackle different classes of fires in their early stages, potentially preventing significant damage to equipment and materials. Class D fire extinguishers are necessary for facilities like metal fabricators or chemical manufacturers that handle combustible substances. Class ABC-rated extinguishers offer comprehensive protection in environments with electrical equipment or flammable liquids, making them versatile for mixed-use industrial spaces.
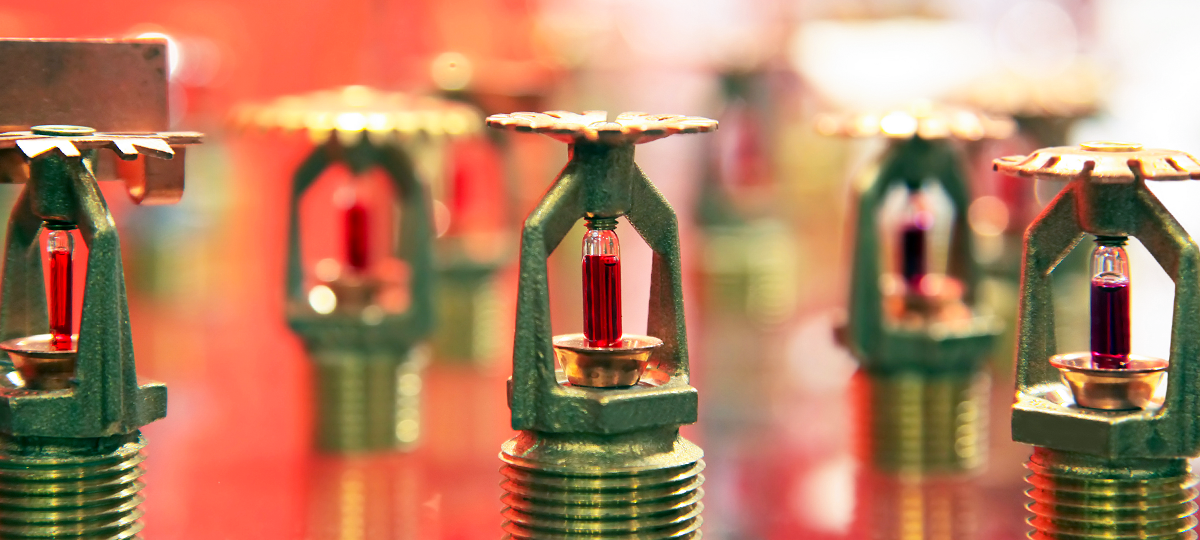
Manufacturing environments like electronics manufacturers or food processors often contain equipment and materials that water would damage or render completely useless. While cost-effective, traditional water-based sprinkler systems can damage machinery and disrupt production. In such cases, chemical-based fire suppression systems that depend on dry or wet chemicals, foam, or inert gases are more appropriate for mitigating industrial fire risks without causing secondary damage.
Balancing production demands with the need for top-notch fire safety in manufacturing and industrial environments can be challenging. That’s where FSS Technologies comes in. Our expert technicians work with you to design, install, and maintain commercial fire safety systems tailored to your needs. No two factories are the same, and we treat your fire protection with the same precision you apply to your operations, from setup to inspections and everything in between. Contact us today to see how we can enhance your facility’s fire safety.